Antibiotic-Resistant Superbugs Could Spread In Clinics, According To A Research
Nikki Attkisson | Last Updated : July 13, 2021As per the latest research, antibiotic drugs are again in trouble due to the presence and spread of a superbug that can easily counter these drugs and still spread at a considerable rate. The research was conducted by the experts to understand the spread of infection among patients from clinics and medical centers which have been a part of the debate for since long. This research has again made the experts go for another option for cleaning clinics and keep them free from such infections.
Antibiotic-Resistant Superbugs Could Spread In Clinics, According To A Research
As per the latest report introduced at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) kept internet this year, water-jet nozzles throughout electrified restrooms frequently in use in Japan as well as both these sections of Asia could be ponds for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) in clinics, raising the chances of hazardous bacteria transmitting between sick people.
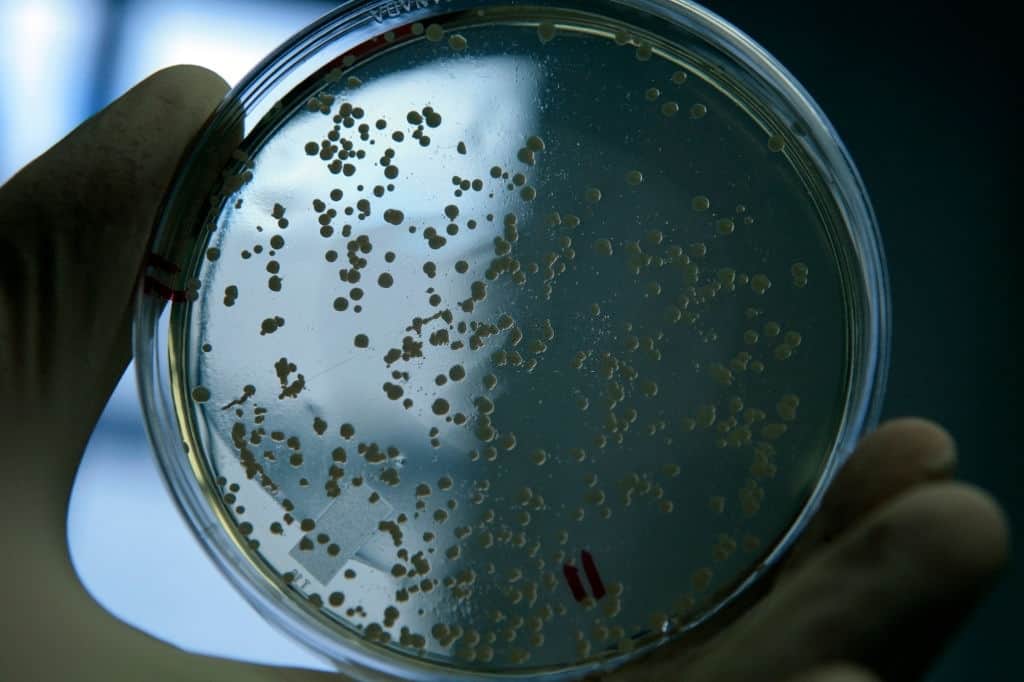
That is the earliest case of institutional infections linked to electrical bathrooms, but it may have huge consequences for disease prevention said the study’s lead author, Dr. Itaru Nakamura of Tokyo Medical University Hospital in Japanese. “Clinic liquid nozzles are a cause of bacterium cross-contamination, further treatments like changed personal cleanliness practices & bathroom cleaning standards might be required to reduce the transfer of infection between medical professionals & consumers.
Over 80percent of Japanese homes have electrical toilets featuring built-in bidets that wash mechanically. The major innovation is a pencil-sized nozzle that emerges from beneath the bathroom floor & flushes liquid both cleanse a tank & wipe the bottoms. In addition, the nozzles are ego, washing oneself pre and post-use.
P. aeruginosa is found in dirt in water, yet it might flourish on damp materials in clinics, causing opportunistic illnesses in fragile and unwell people that might progress to existence illnesses such as influenza or septic.
Due to the widespread use of antibiotics, microorganisms had developed the capacity to survive efforts to cure illnesses using medications that would have destroyed him previously. MDRP bacterial illnesses were growing increasingly frequent in both the public & clinics. The death risk of persons afflicted by such outbreak variants is twice those of individuals afflicted by treatment-resistant variants.
During Sep 2020 and Jan 2021, scientists at Tokyo Medical University Clinic evaluated the occurrence of multidrug-resistant microorganisms retrieved again through waterjet nozzle on electrical bathrooms in a histopathology unit.
Our researchers conducted and over ten trips to collect specimens off moisture nozzles in electrical bathrooms used by 3 MDRP individuals, all of whom had pericardial effusion. MDRP isolates had to be resistant to at minimum 2 medicines like vancomycin, meropenem, amikacin, and ciprofloxacin.
Researchers used molecular identification methods to examine if the MDRP infections of the 3 affected individuals are identified as the MDRP strain obtained from the bathroom faucets in the surroundings. Researchers discovered that the specimens are identical, having strain ‘ST235’ predominating in all of them, implying that client exchanges are taking place.
“These results suggest the multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa germs are getting communicated inside the client population, but, more importantly, because the disease might be propagated inside clinics via infected electrical bathroom nozzle,” Dr. Nakamura explains. “We could restrict the transmission of such diseases through excellent medical cleanliness, that involves soap and water and environment cleanliness, particularly in situations when people’ immunological responses were impaired.”
The researchers emphasize this is modest research conducted on a solitary medical unit. Researchers however pointed up a few flaws, such as the fact because their genomic study couldn’t tell if the transference is between a person to the water-jet nozzles or by the injectors to the people.
Read More: BioFit Reviews
With over 15 years as a practicing journalist, Nikki Attkisson found herself at Powdersville Post now after working at several other publications. She is an award-winning journalist with an entrepreneurial spirit and worked as a journalist covering technology, innovation, environmental issues, politics, health etc. Nikki Attkisson has also worked on product development, content strategy, and editorial management for numerous media companies. She began her career at local news stations and worked as a reporter in national newspapers.
