Exercise Tolerance Test – Simple Test To Inspect Your Heart
Nikki Attkisson | Last Updated : January 27, 2022A 20 minutes test performed to analyze the complete behavior of your heart is the Exercise Tolerance Test. ETT is a form of stress test and helps to detect abnormalities in the heart’s rhythm. It is a noninvasive test performed in a controlled environment to check the cardiac system’s response to physical activity.
What Are The Other Names Of ETT?
Exercise Tolerance Test can also be called Exercise testing, Stress test ECG, Cardiopulmonary exercise test, and stress testing treadmills.
What Is The Principle Of ETT?
Exercise Tolerance Test falls under Bruce protocol. Robert A. Bruce who is considered the “father of exercise physiology” published this as a standardized protocol in 1963. Physicians measure the heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure of the patient while performing exercise through an electrocardiogram. Electrical signals from the heart are recorded by the sensors of the electrocardiogram every time it beats. This helps to graphically analyze the performance of the heart.
What Are The Types Of Exercise Tolerance Tests?
ETT are of various types. They are:
- Exercise Stress Echocardiogram.
- Microvolt T-Wave Alternans Stress Test.
- Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram.
- Maximal Oxygen Consumption Test.
- Myocardial Perfusion Stress Test.
When Is The Exercise Tolerance Test Recommended?
ETT is generally recommended for patients with chest pain, irregular heartbeat, history of cardiac surgeries, undergoing vascular surgery, patients with active cardiac symptoms, Patients with shortness of breath, and general health checkups.
What Is The Use Of ETT?
The purpose of the Exercise Tolerance Test can be elaborated in a broad range. The following uses are:
- To detect electrical signals from the heart during exercise.
- To figure out cardiac rhythm abnormalities.
- To monitor the activity of the heart.
- To identify the occurrence of coronary artery disease.
- To estimate heart rate and energy usage.
- To evaluate effort tolerance and physical capacity.
- To assess post-surgical cardiac stress.
- To predict cardiovascular happenings.
- To measure oxygen uptake by the body.
What Are The Limitations Of ETT?
ETT is not completely reliable. The possibilities of false results are high that it can detect abnormalities with healthy heart patients and vice versa. This test cannot be performed by people with preexisting health issues. Doctors do not completely rely on these test results and use this as a coexisting test.
What Are The Preparations For The Test?
A set of guidelines and instructions are provided by the doctors to take up this test, that is to avoid intake of heavy meals hours before the commencement of the test, follow loose-fitting clothes, avoid caffeine consumption, wear comfortable shoes, and avoid smoking or alcohol consumption before the test. Patients are permitted to intake their regular medications.
How Is The Exercise Tolerance Test Performed?
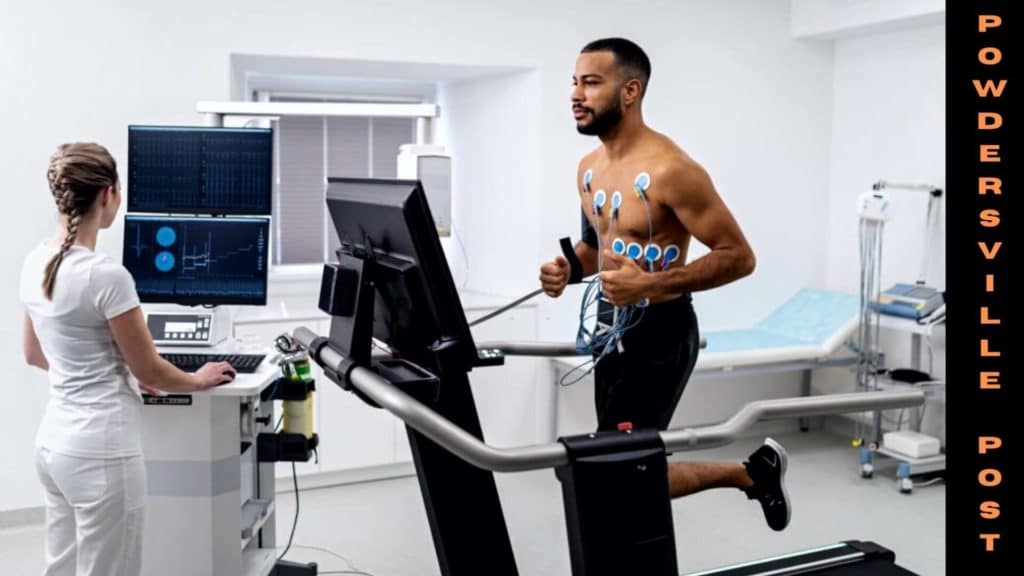
The first step in this is to make the skin ready for performing ETT. Hairs above the skin are shaved off to prevent signal interruptions as the Exercise Tolerance Test is performed by placing electrodes directly onto the skin. In some cases, the superficial layer of the skin is removed to reduce the resistance.
An ECG machine is connected to the electrode to measure the electrical signals from the heart each time it beats. Before the commencement of the exercise, results of blood pressure and ECG are saved. Then you will be asked to perform exercises like treadmilling or riding a stationary exercise bike.
During exercise, blood pressure and heart rate will be measured. ECG track down is done while performing an exercise from lower to increased levels of speed in treadmills. The pace of the exercise is simple in the initial stages and deliberately made difficult with time. After the termination of the test, ECG, heart rate, and blood pressure are computed.
Can The Test Be Terminated In Between?
Yes, in some cases emergencies the tests can be ended considering the patient’s health. Some situations when the test is terminated are:
- A patient has an abnormal heart rate
- Drastic differences in ECG
- Patient has tremendously varying blood pressure
- Patient feels dizzy.
- Patient asks for rest
How To Interpret The Results?
The results are evaluated with the recorded blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG readings. By considering the above records the result can be obtained in the following way:
Positive: It is also called abnormal. Here the patient is identified with some underlying heart illness.
Negative: It is called normal. Here there is no detection of any evidence of heart disease.
Inconclusive: It is called uninterpretable. This is caused by improper functioning of the equipment or termination of the test before completion. Heart condition is not determined in this case.
Goal achieved: This is for fitness check-ups or post-surgical stress check-ups
What Are The Risks Involved In An Exercise Tolerance Test?
ETT is a noninvasive test that is safe to undergo. But there are possibilities for some kind of complications to occur during the test. Some of them are abnormal heart rate and blood pressure levels. They get normal with rest but can provoke heart attacks in extremely rare cases.
What Are The Alternatives To ETT?
Some other tests are even performed for patients to check their hearts health if the patient cannot undergo ETT: They are:
- Computerized tomography (CT) coronary scan.
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
- Dobutamine stress echocardiogram.
- Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET)
- Myocardial perfusion scan.
- Dopamine infusion test.
- Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
With over 15 years as a practicing journalist, Nikki Attkisson found herself at Powdersville Post now after working at several other publications. She is an award-winning journalist with an entrepreneurial spirit and worked as a journalist covering technology, innovation, environmental issues, politics, health etc. Nikki Attkisson has also worked on product development, content strategy, and editorial management for numerous media companies. She began her career at local news stations and worked as a reporter in national newspapers.
