Autoimmune Disorder: A Comprehensive Approach!
Dr. Ricardo Alvarez | Last Updated : August 13, 2022According to the National Institute of Health, autoimmune disorders affect roughly 50 million Americans every year, making them some of the most common and prevalent illnesses in the country.
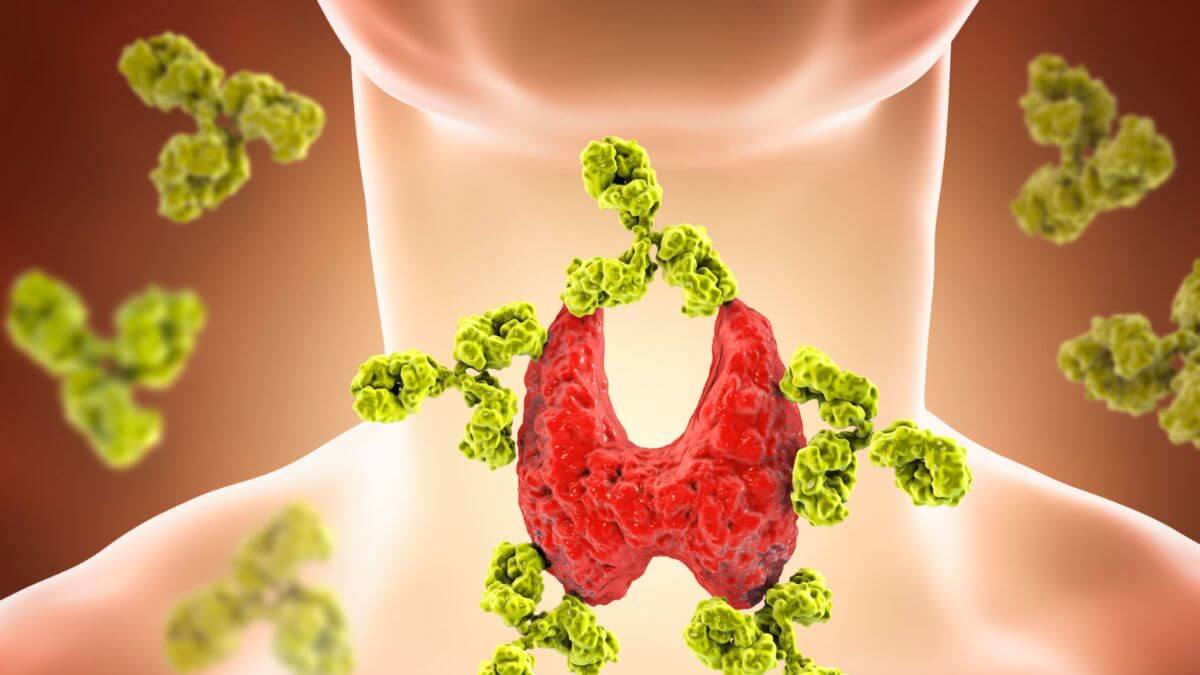
Autoimmune disorders are caused by your immune system attacking healthy cells, organs, and tissue within your body.
This can have various debilitating effects on your quality of life, so it’s important to treat them with the respect they deserve and do everything you can to prevent the onset of an autoimmune disorder.
An Introduction to Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune disorders usually present themselves in one of two ways: either as an overactive immune system or an underactive immune system.

The autoimmune disease most commonly affects women, but anyone can get an autoimmune disease at any age. That being said, those living with autoimmune disorders share the experience of trying to keep themselves — and their bodies — healthy while the immune system appears to be working against them.
Although anyone can develop an autoimmune disease, women are more likely than men to be affected. Autoimmune diseases can affect almost any part of the body, and they vary in their severity.
Some people with autoimmune diseases experience only mild symptoms, while others may have to deal with severe, chronic, or even life-threatening symptoms. There is no cure for autoimmune disease, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Oftentimes, these treatments include prescription medications, supplements, physical therapy, relaxation techniques, stress management techniques, and exercise.
A few examples of treatment options include medications such as methotrexate (MTX), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), prednisone (PRED), cyclosporine (CSP), and biologics such as Rituximab and Remicade; alternative therapies such as massage therapy; cognitive behavioral therapy;
physical therapies like stretching exercises; lifestyle changes such as yoga or Tai Chi; dietary changes like avoiding gluten or adopting a Paleo diet free from processed foods containing inflammatory ingredients; stress management techniques including meditation and mindfulness techniques.
What is an Autoimmune disorder?
An autoimmune disorder is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body. This can happen when the immune system mistakes healthy cells for foreign invaders and starts to destroy them.
Autoimmune disorders can affect any part of the body, but most commonly involve the skin, joints, muscles, and connective tissues.
There are more than 80 different types of autoimmune disorders, each with its own set of symptoms. Many people with autoimmune disorders experience fatigue, joint pain, and muscle aches.
Some also have problems with their digestive system, which can lead to diarrhea or constipation.
In some cases, autoimmune disorders can be life-threatening. Treatment for autoimmune disorders typically involves medication to suppress the immune system and relieve symptoms.
How do Autoimmune Disorders Start?
The body’s immune system is designed to protect us from foreign invaders, like bacteria and viruses. But sometimes, for reasons we don’t yet understand, the immune system goes awry. It attacks healthy cells in the body by mistake.
This can happen in one of two ways: Either the immune system makes too much of one type of protein (autoantibody) that attacks healthy cells, or it doesn’t make enough of a protein that normally helps keep the immune system in check. Either way, when the immune system is out of balance, it can lead to autoimmune disease.
There are more than 80 different autoimmune disorders, and they can range from mild to life-threatening. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis (MS), and psoriasis. With MS, for example, one of your body’s proteins targets cells in your brain and spinal cord by mistake.
When these proteins attack healthy cells in your central nervous system, you may experience symptoms such as numbness or weakness in parts of your body or loss of vision. These diseases are incurable; however, there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms.
What are some common Autoimmune Disorders?
There are many different types of autoimmune disorders, each with its own set of symptoms.
The most common autoimmune disorders include Hashimoto’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, psoriasis, and type 1 diabetes.
Is Autoimmune Disease Serious?
Autoimmune disease is often viewed as not being that serious. But for the millions of Americans who suffer from these conditions, the invisible symptoms can be debilitating. Autoimmune disease is serious and the risk factors are many. From genetics to environmental factors, there are a variety of ways one can develop an autoimmune disorder.
There are tests you can take to determine your level of autoimmunity in certain areas, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. If you believe you may have an autoimmune disorder, it’s important to get tested by your doctor first before self-diagnosing.
For example, celiac disease is often misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome because people don’t know what celiac disease looks like on a blood test and feel better after following a gluten-free diet. It is also possible to experience positive test results but no signs of any symptoms, which would warrant further testing.
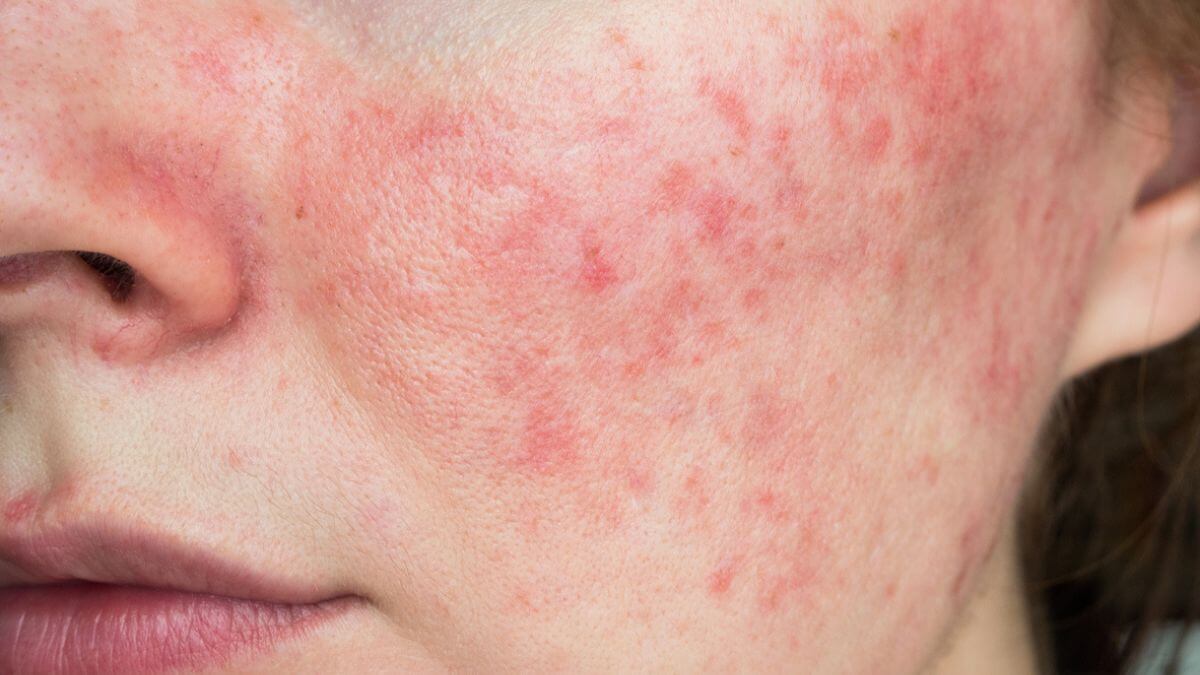
Lupus sufferers often look for clues in their skin (such as color) and other joints (joint pain). One early sign of lupus is frequent bruising without apparent cause.
Arthritis sufferers might notice joint pain or stiffness that worsens over time, fatigue and soreness when they wake up in the morning, and problems working out at the gym because of joint pain.
In general, most autoimmune disorders start presenting symptoms around the age of 20-30 years old and affect women more than men. That being said, it is important to talk to your doctor about treatment options before deciding that you have an autoimmune disorder. Options range from medication to surgery depending on the severity of your condition.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases can be difficult to diagnose because they often mimic other illnesses. fatigue, joint pain, and fever are all common symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Other symptoms can include gastrointestinal issues, skin problems, and headaches.
In some cases, autoimmune diseases can also lead to organ damage. A good example is a lupus, which can affect the heart, lungs, kidneys, and central nervous system.
In many cases, the symptoms of an autoimmune disease will worsen over time until it becomes too difficult for a person to manage their daily life. Treatment for autoimmune disease may involve taking drugs that suppress the immune system or medications that help control inflammation in the body.
However, many people choose not to treat their condition at all or limit treatment if they are experiencing few or no symptoms.
Can Autoimmune Diseases be cured?
Autoimmune diseases cannot be cured but can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing an autoimmune disease, as each person experiences the condition differently.
However, some tips for managing autoimmune diseases include eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, and exercising regularly. If you have an autoimmune disease, it’s important to work with a healthcare team to create a treatment plan that works for you.
Working together, you can find the right balance of medications and lifestyle changes to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Here are four steps to get started on your journey towards wellness:
✔️Know what causes autoimmune diseases and how they affect you;
✔️ Find the right doctor or team of doctors who will provide individualized care;
✔️ Get involved in research studies that may provide new insights into better treatments;
✔️Consider complementary therapies such as yoga, acupuncture, massage therapy, and mindfulness meditation.
How do you treat Autoimmune Disease?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best way to treat an autoimmune disease will vary from person to person. However, there are some general principles that can help guide your treatment plan.
- First and foremost, it’s important to work with a healthcare team that you trust and feel comfortable with.
- don’t be afraid to advocate for yourself – know your rights and what you need in order to get the best possible care.
- be willing to experiment until you find what works for you.
- give yourself time to heal both physically and emotionally.
- make sure to take care of yourself – mind, body, and soul.
- remember that there is hope and healing available for everyone who has an autoimmune disorder!
More From Powdersville Post:
✔️ UVA Health Introducing New Method For Pain Relief!
✔️ Researchers Develop A Test To Detect Over 50 Genetic Disorders
What diet is best for Autoimmune Disease?
There is no one-size-fits-all diet for people with autoimmune diseases, as each person’s condition is unique. However, there are some general dietary guidelines that may help to lessen symptoms and promote healing.
In general, it is best to eat whole, unprocessed foods (plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains). It is also important to get enough protein, as well as healthy fats such as Omega-3s.
It is also important to avoid trigger foods. Common trigger foods include gluten, dairy, soy, sugar, eggs, corn, and nightshade vegetables. However, triggers vary from person to person so it is important to figure out what works for you.
A good way to do this is through an elimination diet. Eliminate certain foods or food groups (such as gluten) and see how your body reacts after three weeks before reintroducing them into your diet.
If symptoms return, then you know that these foods are not the cause of your problem. You can then start to add new food groups back in slowly to find out what might be causing the reaction.
The most important thing is to listen to your body and experiment with different diets until you find something that feels right for you!
Final Thoughts
Autoimmune diseases are often called invisible illnesses because the symptoms are not always apparent to others. This can make it difficult for friends and family to understand what you’re going through.
You may feel like you have to explain your symptoms all the time or justify why you can’t do certain things. It can be frustrating and isolating.
There are millions of people living with autoimmune diseases. And there is hope. With treatment, many people are able to manage their symptoms and live full, happy lives.
If you’re struggling, reach out to a support group or talk to your doctor.
Summary
An autoimmune disorder, or autoimmunity, occurs when the immune system malfunctions and begins to attack healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 known autoimmune disorders, many of which affect the nervous system and produce symptoms that range from mild to debilitating.
Frequently Asked Questions
Dr. Ricardo Alvarez was a former Medical professor and faculty at Harvard Medical school. After resigning, now he is practicing as a general physician who deals with the diagnosis and treatment of general health problems and disorders. He earned his MS and PhD from Columbia University. Ricardo Alvarez completed his undergraduate education from an accredited medical college under the University of London and completed his training from AMCAS and is a doctor with earned board certification.